Difference between monetary and fiscal policy
They are both used to pursue policies of higher economic growth or controlling inflation.
Monetary policy
Monetary policy is usually carried out by the Central Bank/Monetary authorities and involves:
- Setting base interest rates (e.g. Bank of England in UK and Federal Reserve in the US)
- Influencing the supply of money. E.g. Policy of quantitative easing to increase the supply of money.
How monetary policy works
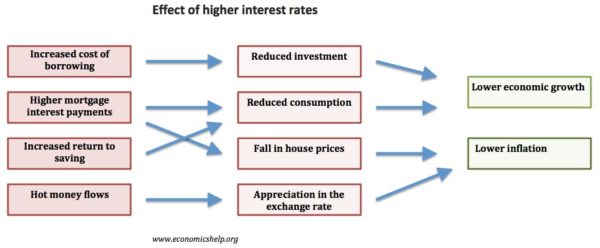
- The Central Bank may have an inflation target of 2%. If they feel inflation is going to go above the inflation target, due to economic growth being too quick, then they will increase interest rates.
- Higher interest rates increase borrowing costs and reduce consumer spending and investment, leading to lower aggregate demand and lower inflation.
- If the economy went into recession, the Central Bank would cut interest rates.
- See also: Cutting interest rates
Fiscal policy
Fiscal policy is carried out by the government and involves changing:
- Level of government spending
- Levels of taxation
- To increase demand and economic growth, the government will cut tax and increase spending (leading to a higher budget deficit)
- To reduce demand and reduce inflation, the government can increase tax rates and cut spending (leading to a smaller budget deficit)
Example of expansionary fiscal policy
In a recession, the government may decide to increase borrowing and spend more on infrastructure spending. The idea is that this increase in government spending creates an injection of money into the economy and helps to create jobs. There may also be a multiplier effect, where the initial injection into the economy causes a further round of higher spending. This increase in aggregate demand can help the economy to get out of recession.
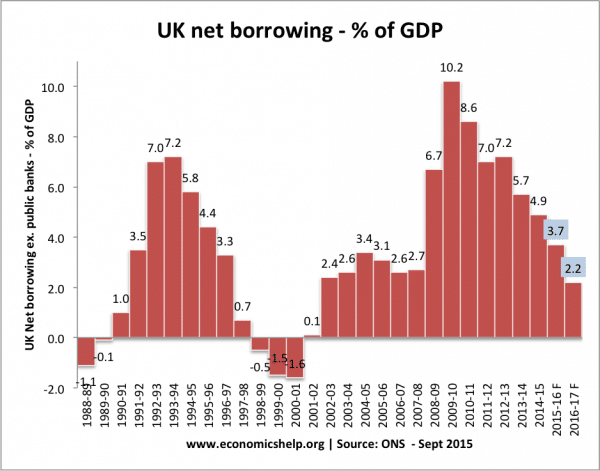
This shows that in 2009/10 the UK ran a budget deficit of 10% of GDP. This was caused by the recession and also the government’s attempt to provide a fiscal stimulus (VAT tax cut) to try and get the economy out of recession.
If the government felt inflation was a problem, they could pursue deflationary fiscal policy (higher tax and lower spending) to reduce the rate of economic growth.
Which is more effective monetary or fiscal policy?
In recent decades, monetary policy has become more popular because:
- Monetary policy is set by the Central Bank, and therefore reduces political influence (e.g. politicians may cut interest rates in the desire to have a booming economy before a general election)
- Fiscal policy can have more supply side effects on the wider economy. E.g. to reduce inflation – higher tax and lower spending would not be popular, and the government may be reluctant to pursue this. Also, lower spending could lead to reduced public services, and the higher income tax could create disincentives to work.
- Monetarists argue expansionary fiscal policy (larger budget deficit) is likely to cause crowding out – higher government spending reduces private sector expenditure, and higher government borrowing pushes up interest rates. (However, this analysis is disputed)
- Expansionary fiscal policy (e.g. more government spending) may lead to special interest groups pushing for spending which isn’t really helpful and then proves difficult to reduce when the recession is over.
- Monetary policy is quicker to implement. Interest rates can be set every month. A decision to increase government spending may take time to decide where to spend the money.
However, the recent recession shows that monetary policy too can have many limitations.
- Targeting inflation is too narrow. During the period 2000-2007, inflation was low but central banks ignored an unsustainable boom in the housing market and bank lending.
- Liquidity trap. In a recession, cutting interest rates may prove insufficient to boost demand because banks don’t want to lend and consumers are too nervous to spend. Interest rates were cut from 5% to 0.5% in March 2009, but this didn’t solve recession in the UK.
- Even quantitative easing – creating money may be ineffective if banks just want to keep the extra money on their balance sheets.
- Government spending directly creates demand in the economy and can provide a kick-start to get the economy out of recession. Thus in a deep recession, relying on monetary policy alone, may be insufficient to restore equilibrium in the economy.
- In a liquidity trap, expansionary fiscal policy will not cause crowding out because the government is making use of surplus saving to inject demand into the economy.
- In a deep recession, expansionary fiscal policy may be important for confidence – if monetary policy has proved to be a failure.
Related
- Policies for reducing unemployment
- UK Monetary Policy
- Criticisms of fiscal policy
- Fiscal policy




